Body Temperature Screening – Which Method to Go For?
 With the coronavirus pandemic still raging around the world, the mandate is clear: follow the necessary protocols and focus on prevention than cure. For customer-facing businesses/organizations, this involves body temperature screening, spatial distancing, activating heightened hygiene measures, and setting up a Covid-19 responder. While most of these are fairly manageable, the body temperature part can get tricky.
With the coronavirus pandemic still raging around the world, the mandate is clear: follow the necessary protocols and focus on prevention than cure. For customer-facing businesses/organizations, this involves body temperature screening, spatial distancing, activating heightened hygiene measures, and setting up a Covid-19 responder. While most of these are fairly manageable, the body temperature part can get tricky.
Why? Because a thermal imaging system for human fever screening is the most accurate way to screen both workers and customers in a physical setting. This calls for a need to choose and set up the right method according to the type and setting of the business/organization. While modern body temperature thermal cameras provide accurate data and detailed insights, setting it up can often be challenging. Moreover, handheld temperature cameras may not always be feasible and effective, especially when the purse is tight.
A solution to this quandary can be derived by looking at the two main methods of body temperature screening – handheld thermometers and body temperature thermal cameras. Here’s an in-depth look at the two popular methods as well as a business owner’s guide to choosing between them based on efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and convenience.
Why is Body Temperature Screening Necessary?
Around the world, it’s either a government-backed mandate or common sense (or both) that makes body temperature screening necessary. If it’s the CDC in the United States of America, it’s some other healthcare body in another country that has mandated temperature screening in commercial and public places as a measure to prevent the spread of the coronavirus. Even if there is no mandate present, businesses – both small and large – opt to have a basic setup in place to keep everyone safe. Since fever i.e., a body temperature of above 100.4 degree-Fahrenheit, is one of the major and easily identifiable symptoms of Covid-19, temperature screening acts as a helpful hand.
The idea is to screen everyone – from workers to managers to customers to vendors – entering a business facility and prevent individuals with fever from interacting with anyone. Healthcare bodies working with Covid-19 data so far suggest that individuals with fever should isolate themselves to prevent the spread, should they have the virus in their system. Such a person, if detected, can be isolated and treated. This type of active detection and isolation can go a long way in plugging the spread.
While body temperature screening is only one of the ways to detect individuals who may be infected with SARS-CoV-2, it is a joint effort of everyone involved (including the authorities) to reduce the spread. The point, however, is in the need for businesses to have a basic setup.
Modern Methods of Measuring Body Temperature
There are primarily two modern methods by which you can measure body temperature in humans: handheld thermometers and thermal cameras.
- Handheld thermometer – a small device that uses infrared to detect temperature. It is often shaped like a gun and needs to be pointed to the body (forehead or outside of a hand) of a person by an operator. The range is between one to four feet
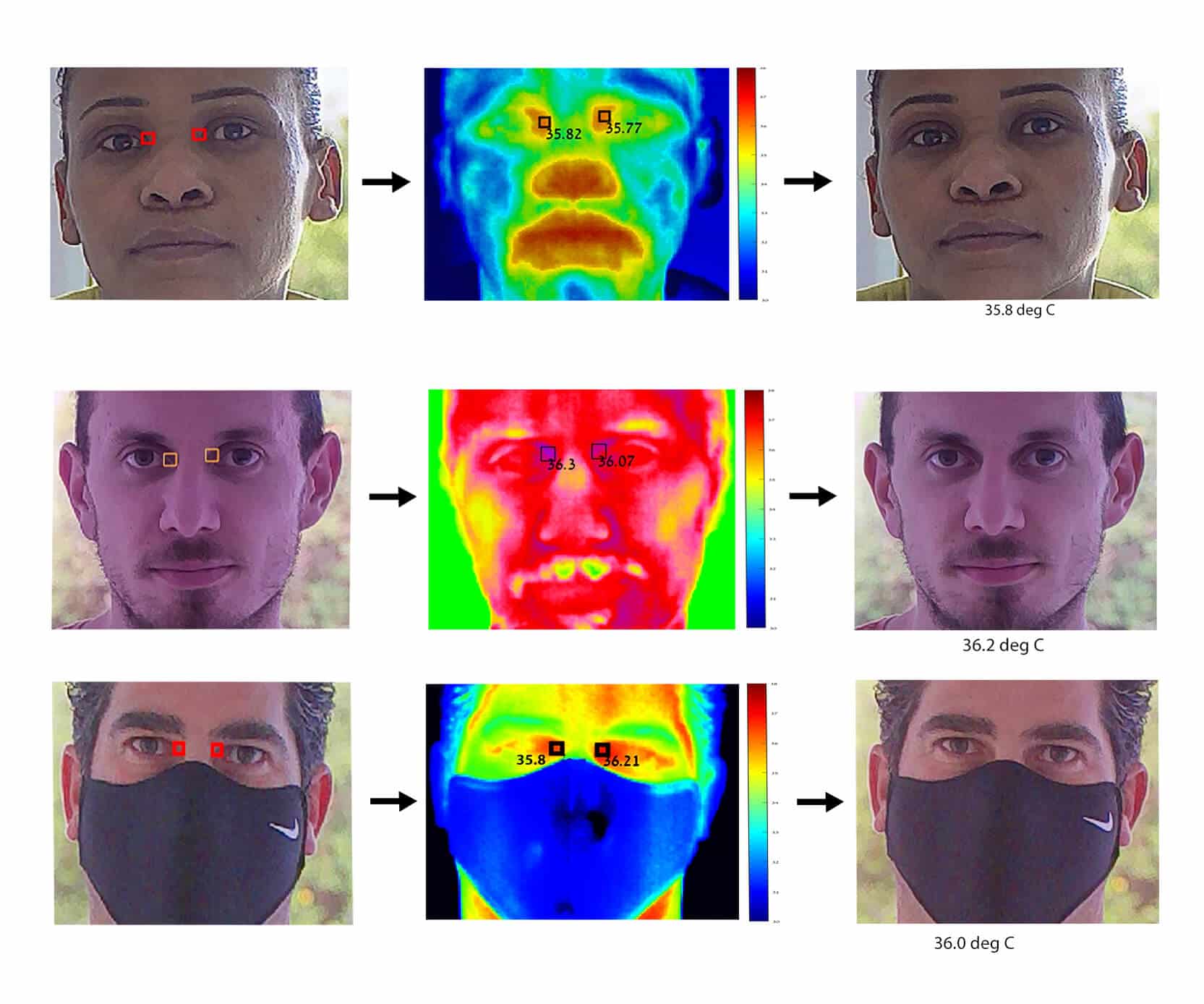
- Thermal camera – Widely used for elevated body temperature (EBT) screening, it uses thermal imaging technology to detect body temperature by focusing on a person’s tear ducts (the inside end of the eyes). It does not require an operator and can be placed at a maximum distance of 15 feet away from the person being screened.
Different types of screeners exist even across these two types in the commercial market. One example is CI Systems TCam – an advanced temperature screening camera that brings together the power of thermal imaging and processing in a single, small device. It is an advanced mechanism that can measure and record data while ensuring anonymity for the people being screened.

FIGURE 1 – CI Systems TCam: elevated body temperature screening camera
It can be said that thermal imagers are extended versions of handheld thermometers. Yet the way they work and the advantages they bring to the table are different. Moreover, the need for contactless body temperature screening has brought the focus on thermal imagers like TCam for domestic applications as well. Till a few years ago, thermal imagers were restricted to industrial applications. They were and are installed in warehouses, assembly plants, and factories to enable remote sensing-based infrared temperature detection. As opposed to a human body, they detected the temperature of systems and facilities as a whole.
This makes it important to understand how thermal imaging works and how cutting-edge contactless body temperature screening systems like TCam help in executing safety measures against Covid-19.
Thermal Imaging Systems – How Do They Work?
In comparison with an infrared thermometer, a thermal imager uses additional components such as processors, visual cameras, storage, and heat reference points to provide more insights. It can detect, measure, store, and process data that can be useful to gather insights. As a tool against Covid-19, its biggest advantages are its ease of setup, convenient use, and contactless measurement.
Take the case of how TCam can be set up and help in body temperature screening in a business facility like a supermarket or a restaurant:
- Setting up of TCam using a computer or as a standalone device (that can be directly connected to the Internet).
- A person walks into a facility and stands in front of TCam.
- TCam automatically detects the tear ducts and measures the temperature in the areas. It also captures a thermal and visible image and stores them in the internal storage.
- If the detected temperature is above the threshold preset temperature, TCam will alert the person with a red light. Measurement using a medical thermometer is recommended. In case the temperature is below the preset, the tool will display a green light.
All of this happens in a matter of seconds, which is an important function to consider for businesses that see large footfalls. Although social distancing is key to prevent the spreading of coronavirus, thermal imaging tools like TCam can help screen a large number of people quickly and without the need of an operator.
But another question that can be asked at this juncture is: how effective are these body temperature detectors?
Here’s a quick look at the advantages of industry-grade thermal sensors.
Advantages of Body Temperature Thermal Cameras
A list of the merits of using thermal cameras:
- High accuracy
- Real-time data processing, data storage
- Radiometric accuracy of +/- 0.3 deg Celsius in most tools such as TCam
- Internet connectivity
- Ability to take an anonymous snapshot of the person being screened
- Time and date stamps
All of this makes thermal cameras more reliable than a handheld thermometer. However, the decision of choosing between the two should ideally depend on the nature and extent of the business. For example, a supermarket experiencing a footfall of 100 customers per hour may find thermal cameras more effective. On the other hand, a pharmacy that sees 100 customers in a span of an entire day should consider using an infrared thermometer for better cost-effectiveness.
Why Thermal Cameras Are Better in This Covid Age?
The main argument for using thermal cameras is that they do not require a person to operate unlike when using a thermometer. Since Covid-19 spreads via air, the idea is to avoid human contact whenever possible. This makes thermal cameras a better alternative.
Such tools can be installed by a single person in a matter of a few hours. And tools like TCam do not even require a technician for installation. It can be installed and operated by a layperson by following the instruction manual.
Here’s an illustration of how easy it is for a person to use a thermal camera installed for elevated body temperature screening.
-min_20210307154336.924.jpg)
FIGURE 2 – illustration of a person using TCam
Another advantage of using thermal imaging systems for human fever screening is comparative cost-effectiveness. In large business units, an operator handling an infrared thermometer will not only require a PPE kit but also a backup (person), a disinfection system, and associated resources. Annually, this can set the business back by a lot of money.
On the other hand, installing and using a thermal camera is a one-time cost. The only two resources needed post installation is power and data storage/processing. Moreover, the latter is not a daily task and can be handled at the end of the month if a proper inventory is to be maintained. Establishments like large hospitals and shopping malls may need to record this type of data, especially if they are working with the authorities.
So, which method to go for?
The answer seems to be clear. If accuracy, convenience, and cost-effectiveness are the major parameters in the selection, a remote sensing body heat camera like TCam will be the best option. If the business is a small-scale establishment with infrequent patronship, a handheld thermometer will be enough.
Per maggiori informazioni sui prodotti visita il sito:


